ANGSD: Analysis of next generation Sequencing Data
Latest tar.gz version is (0.938/0.939 on github), see Change_log for changes, and download it here.
Abbababa: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Performs the abbababa test also called the D-statistic. This tests for ancient admixture (or wrong tree topology). As all methods in ANGSD we require that the header of the BAM files are the same. | Performs the abbababa test also called the D-statistic. This tests for ancient admixture (or wrong tree topology). As all methods in ANGSD we require that the header of the BAM files are the same. | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 3 January 2014
Performs the abbababa test also called the D-statistic. This tests for ancient admixture (or wrong tree topology). As all methods in ANGSD we require that the header of the BAM files are the same.
<classdiagram type="dir:LR">
[BAM files{bg:orange}]->[Sequence data|Random base]
[sequence data]->[*.abbababa|ABBA and BABA couts file{bg:blue}] </classdiagram>
<classdiagram type="dir:LR">
[*.abbababa|ABBA and BABA couts file{bg:blue}]->jackKnife.R[D stat and Z scores{bg:blue}]
</classdiagram>
Method
Brief Overview
> ./angsd -doAbbababa -------------- analysisAbbababa.cpp: -doAbbababa 0 run the abbababa analysis -rmTrans 0 remove transitions -blockSize 5000000 size of each block in bases -ans (null) fasta file with outgroup
This function will counts the number of ABBA and BABA sites
Options
- -doAbbababa 1
- sample a random base at each position.
- -rmTrans
Remove transitions (important for ancient DNA)
- -blockSize [INT]
Size of each block. Choose a number that is higher than the LD in the populations. For human 5Mb (5000000) is usually used.
- -anc [fileName.fa]
Include an outgroup in fasta format.
- -doCounts 1
use -doCounts 1 in order to count the bases at each sites after filters.
In order to do fancy filtering of bases based on quality scores see the Allele counts options.
Output
- .abbbababa
Output: Each lines represents a block with a chromsome name (Column 1), a start position (Column 2), an end postion (Column 3). The new columns are the counts of ABBA and BABA sites. For each combination of 3 individuals (H1,H2,H3) two columns are printed. These number served as input to the R script called jackKnife.R
Example
Create a fasta file bases from a random samples of bases.
head -n5 bam.filelist > smallBam.filelist ./angsd -out out -doAbbababa 1 -bam smallBam.filelist -doCounts 1 -anc chimpHG19.fa Rscript R/jackKnife.R file=out.abbababa indNames=smallBam.filelist outfile=out
This results in a out.txt file with all the results.
Output
H1 H2 H3 nABBA nBABA Dstat jackEst SE Z NA11830 NA12004 NA12763 269 322 -0.08967851 -0.08967851 0.09006086 -0.9957545 NA11830 NA06985 NA12763 267 298 -0.05486726 -0.05486726 0.122256 -0.4487898 NA12004 NA06985 NA12763 254 243 0.0221328 0.0221328 0.1386198 0.1596655 NA11830 NA11993 NA12763 225 336 -0.197861 -0.197861 0.08514797 -2.323731 NA12004 NA11993 NA12763 217 267 -0.1033058 -0.1033058 0.09471542 -1.090697 NA06985 NA11993 NA12763 242 302 -0.1102941 -0.1102941 0.1241554 -0.8883553 NA12763 NA12004 NA11830 237 322 -0.1520572 -0.1520572 0.1047361 -1.451813 NA12763 NA06985 NA11830 219 298 -0.1528046 -0.1528046 0.1115283 -1.370098
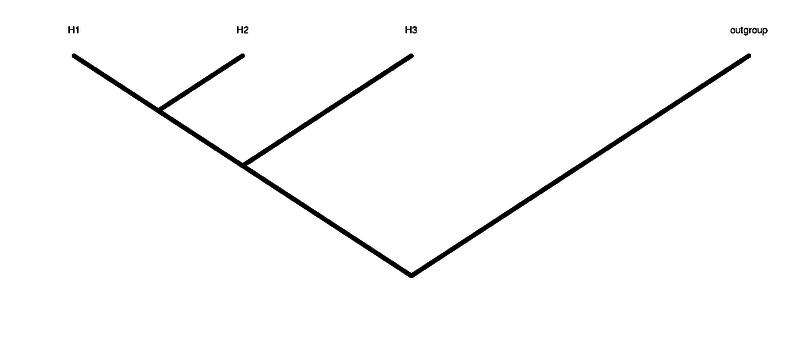
H1 H2 H3 are the 3 individuals in the tree that are not the outgroup. H1 and H2 are the ingroup (see figure of tree above)
nABBA the total counts of ABBA patterns
nBABA the total counts of BABA patterns
Dstat The test statistic: (nABBA-nBABA)/(nABBA+nBABA). A negative value means that H1 is closer to H3 than H2 is. A positive value means that H2 is closer to H3 than H1 is.
JackEst column is another estimate of the abbababa statistic that is bias corrected. This value is extremely similar to the value in the Dstat column
SE is the estimated m-delete blocked Jackknife Standard error of the estimate used to obtain the Z value
Z Z value that can be used to determine the significance of the test. As in Reich et al. an absolute value of the Z score above 3 is often used as a critical value. However, this note that this does not take into account the fact that we perform multiple tests.