ANGSD: Analysis of next generation Sequencing Data
Latest tar.gz version is (0.938/0.939 on github), see Change_log for changes, and download it here.
Abbababa2: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
<classdiagram type="dir:LR"> | <classdiagram type="dir:LR"> | ||
[*.abbababa2|weighted ABBA and BABA counts file {bg:blue}]-->estAvgError.R[*.Observed.txt|D stat and Z scores + Error est and Plots{bg:blue}] | [*.abbababa2|weighted ABBA and BABA counts file {bg:blue}]->->estAvgError.R[*.Observed.txt|D stat and Z scores + Error est and Plots{bg:blue}] | ||
</classdiagram> | </classdiagram> | ||
Revision as of 12:36, 26 August 2016
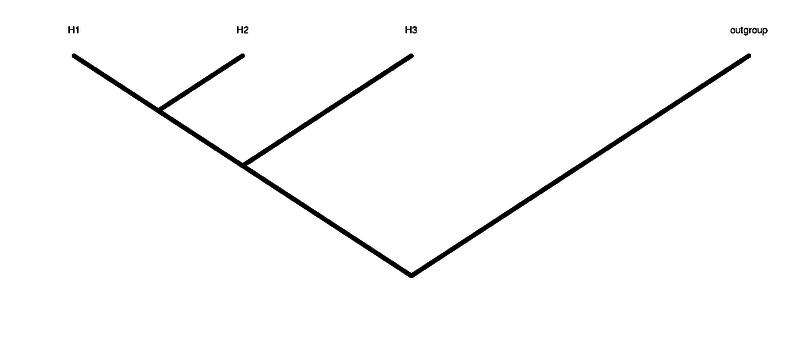
The ABBABABA (multipop) compute the abbababa test (aka D-statistic), that means testing for an ancient admixture (or wrong tree topology). Differently from ABBABABA (D_stat) multiple individuals for each one of the groups are allowed. As all methods in ANGSD we require that the header of the BAM files are the same.
- some of the options only works for the developmental version availeble from github
- if you use -rf to specify regions. These MUST appear in the same ordering as your fai file.
<classdiagram type="dir:LR">
[*.BAM| NGS genomes{bg:orange}]->[Sequence data|All bases or Random bases]
[Sequence data]->[Elaborate multiple genomes per population] [Sequence data]->[*.abbababa2counts|ABBA and BABA intermediate counts file {bg:blue}] [Elaborate multiple genomes per population]->[*.abbababa2|weighted ABBA and BABA counts file {bg:blue}] </classdiagram>
<classdiagram type="dir:LR"> [*.abbababa2|weighted ABBA and BABA counts file {bg:blue}]->->estAvgError.R[*.Observed.txt|D stat and Z scores + Error est and Plots{bg:blue}] </classdiagram>
Method
Brief Overview
> ./angsd -doAbbababa2
--------------
abcDstat2.cpp:
-doAbbababa2 0 run the abbababa analysis
-rmTrans 0 remove transitions
-blockSize 5000000 size of each block in bases
-anc (null) fasta file with outgroup
-sample 0 sample a single base in each individual
-maxDepth 100 max depth of each site allowed
-sizeH1 1 num of individuals in group H1
-sizeH2 1 num of individuals in group H2
-sizeH3 1 num of individuals in group H3
-sizeH4 1 num of individuals in group H4
-enhance 0 only analyze sites where outgroup H4 is non poly
-Aanc 0 set H4 outgroup allele as A in each site
-combFile 0 create an optional *.abbababa2counts file where are printed the
numbers of alleles combinations without having weighted the individuals
This function will counts the number of ABBA and BABA sites.
Options
- -doAbbababa2 1
take all bases at each position.
- -rmTrans [int]
0; use all reads (default), 1 Remove transitions (important for ancient DNA)
- -blockSize [INT]
Size of each block. Choose a number that is higher than the LD in the populations. For human 5Mb (5000000) is usually used.
- -anc [fileName.fa]
Include an outgroup in fasta format.
- -doCounts 1
use -doCounts 1 in order to count the bases at each sites after filters.
- -enhance [int]
1: use only sites where the reads for the outgroup has the same base for all reads.
- -sample [int]
1: sample only one base at each position for every individual 0: all bases at each position are used for the ABBABABA test
- -maxDepth [int]
allows for a maximum depth in each site to avoid overflow of the ABBA BABA counts
- -sizeH* [int]
decide how many individuals are in each group (the file list must contain the BAM files ordered from population 1 to 4). If you are using a fasta file (option -anc) for population H4, leave -sizeH4 at its default value
- -Aanc [int]
1: H4 allele is A in each site.
- -combFile [int]
1: create an intermediate *.abbababa2counts to obtain the allele events before weighting the samples (however, this file is not used for the estimation of the D-statistic).
In order to do fancy filtering of bases based on quality scores see the Allele counts options.
Output
- .abbbababa2
Output: Each line represents a block with a chromsome name (Column 1), a start position (Column 2), an end postion (Column 3). The new columns are the counts of all 256 counted combination of alleles, starting from X0000=AAAA,X0001=AAAC,....,X3333=TTTT, with the correspondence 0=A,1=C,2=G,3=T. This file is used as input for the R script estAvgError.R. Type "Rscript R/estAvgError.R" to see additional options.
- .abbbababa2counts (optional file)
Output: As above each line represents a block with a chromsome name (Column 1), a start position (Column 2), an end postion (Column 3). The new columns are the counts of all 256 counted combination of alleles, starting from X0000=AAAA,X0001=AAAC,....,X3333=TTTT, with the correspondence 0=A,1=C,2=G,3=T. This file is not used as input for the ABBABABA test.
Example
Run the ABBABABA (multipop), without sampling a single allele for each site. We use 2 individuals for each group, thus the smallBam.filelist file contains the 8 file names ordered from population H1 to H4.
# select 8 individuals (suppose they are already in the desired order H1,..,H4) head -n8 bam.filelist > smallBam.filelist #run angsd ./angsd -out out -doAbbababa2 1 -bam smallBam.filelist -doCounts 1 -sample 0 -enhance 0 -sizeH1 2 -sizeH2 2 -sizeH3 3 -sizeH4 2 -combFile 0 #estimate Z score Rscript R/estAvgError.R file=out outfile=outDstat
This results in multiple output files with all the results.
1) a file outDstatStd.txt, that contains the results of the ABBABABA test without applying neither error correction or ancient transition removal
2) a file outDstatNoErrorNoTrans.txt, that contains the results of the ABBABABA test without applying error correction but removing ancient transitions
Output
1)outDstatStd.txt
mean(D) JK-D V(JK-D) Z pvalue nABBA nBABA nBBAA -0.042874 -0.042945 0.000643 -1.690314 0.090968 1697.447933 1704.675933 6374.948767
2)outDstatNoErrorNoTrans.txt
mean(D) JK-D V(JK-D) Z pvalue nABBA nBABA nBBAA -0.042874 -0.042945 0.000643 -1.690314 0.090968 1697.447933 1704.675933 6374.948767
mean(D) The average of test statistics: (nABBA-nBABA)/(nABBA+nBABA), each one calculated for a block of data.
JK-D The estimated test statistic: (nABBA-nBABA)/(nABBA+nBABA) after being bias corrected. This value should be similar to the one in column 1. A negative value means that H1 is closer to H3 than H2 is. A positive value means that H2 is closer to H3 than H1 is.
V(JK-D) estimated m-delete blocked Jackknife variance of the estimator of column 2. It's used to compute the Z-value.
Z Z value that can be used to determine the significance of the test. As in Reich et al. an absolute value of the Z score above 3 is often used as a critical value.
pvalue p-value corresponding to Z for a double-sided standard test. the critical value 0.001 correspond to the value of Z=3.
nABBA the total counts of ABBA patterns
nBABA the total counts of BABA patterns
nBBAA the total counts of BBAA patterns