NgsAdmixv2: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The great thing about NGSadmix is that it is a new method that takes the uncertainty introduced in NGS sequencing data into account when inferring an individual's ancestry by using genotype likelihoods that considers the uncertainty caused by unobserved genotypes. | The great thing about NGSadmix is that it is a new method that takes the uncertainty introduced in NGS sequencing data into account when inferring an individual's ancestry by using genotype likelihoods that considers the uncertainty caused by unobserved genotypes. | ||
As with the other existing software, ADMIXTURE and STRUCTURE, NGSadmix is only sensitive to admixture recent enough to cause structures in the population in terms of differing allele frequencies. Historical admixture events after which many generations has passed in the population, leaves no signature in terms of systematic differences in allele frequencies between individuals and are not a concern in association studies. | |||
[[File:NgsAdmix.png|thumb]] | [[File:NgsAdmix.png|thumb]] | ||
Revision as of 10:32, 25 June 2019
This page contains information about the program called NGSadmix, which is a very nice tool for estimating individual admixture proportions from NGS data. It is based on genotype likelihoods and works well for medium and low coverage NGS data. It is a fancy multithreaded c/c++ program which makes it useful for large datasets.
The great thing about NGSadmix is that it is a new method that takes the uncertainty introduced in NGS sequencing data into account when inferring an individual's ancestry by using genotype likelihoods that considers the uncertainty caused by unobserved genotypes.
As with the other existing software, ADMIXTURE and STRUCTURE, NGSadmix is only sensitive to admixture recent enough to cause structures in the population in terms of differing allele frequencies. Historical admixture events after which many generations has passed in the population, leaves no signature in terms of systematic differences in allele frequencies between individuals and are not a concern in association studies.
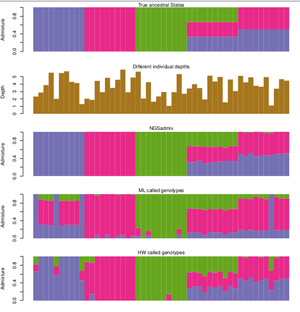
The method was published in 2013 and can be found here: [1]
Software Download
The latest version of NGSadmix is ngsadmix32 from June 25, 2013 and can be downloaded here: [2].
- Older Versions
- The previous version of NGSadmix, ngsadmix31 can be found here: [3].
- Version Log:
- v32 june 25-2013; modified code such that it now compiles on OSX
- v31 june 24-2013; First public version.
Installation
NGSadmix can be installed independently or as a part of ANGSD.
NGSadmix Independent Installation
1. Login to your server using ssh on your terminal window.
2. Create the directory where you will install your software and enter it, such as
mkdir ~/Softwarecd ~/Software
3. Download the source code:
4. Configure, Compile and Install:
g++ ngsadmix32.cpp -O3 -lpthread -lz -o NGSadmix
5. Delete source code to save space:
rm ~/Software/ngsadmix32.cpp
NGSadmix Installation from ANGSD
Run command example
Download the input file
wget popgen.dk/software/download/NGSadmix/data/input.gz
Execute NGSadmix
./NGSadmix -likes input.gz -K 3 -P 4 -o myoutfiles -minMaf 0.05
Detailed Examples and Tutorial
Please refer to the tutorial's page [4]
Parameters
All parameters are set using -par value. For example, to get additional information, you would write -printInfo 1.
./NGSadmix
*** see doc for options/possible ranges/ and further explanation Arguments: -likes .beagle format filename with genotype likelihoods -K Number of ancestral populations Optional: -fname Ancestral population frequencies -qname Admixture proportions -outfiles Prefix for output files -printInfo print ID and mean maf for the SNPs that were analysed Setup: -seed Seed for initial guess in EM -P Number of threads -method If 0 no acceleration of EM algorithm -misTol Tolerance for considering site as missing Stop criteria: -tolLike50 Loglikelihood difference in 50 iterations -tol Tolerance for convergence -dymBound Use dymamic boundaries (1: yes (default) 0: no) -maxiter Maximum number of EM iterations Filtering -minMaf Minimum minor allele frequency -minLrt Minimum likelihood ratio value for maf>0 -minInd Minumum number of informative individuals
Input File
Input files are contains genotype likelihoods in genotype likelihood beagle input file format [5]. We recommend ANGSD for easy transformation of Next-generation sequencing data to beagle format. See Creation of Beagle files with ANGSD
The input file is allowed to be compressed with gzip.
Output Files
Program outputs 3 files.
- PREFIX.log
- PREFIX.fopt.gz
- PREFIX.qopt
- The .log file contains log information of the run. Commandline used for running the program, what the likelihood is every 50 iterations, and finally how long it took to do the run.
- The .fopt.gz file is an compressed file, which contains an estimate of the frequency for each site for all populations.
- The .qopt file contains the admixture proportions for all individuals.
Citation
http://www.genetics.org/content/early/2013/09/03/genetics.113.154138.full.pdf
Skotte, L., Korneliussen, T. S., & Albrechtsen, A. (2013). Estimating individual admixture proportions from next generation sequencing data. Genetics, 195(3), 693–702. doi:10.1534/genetics.113.154138
- Bibtex
- % 24026093
- @Article{pmid24026093,
- Author="Skotte, L. and Korneliussen, T. S. and Albrechtsen, A. ",
- Title="{{E}stimating {I}ndividual {A}dmixture {P}roportions from {N}ext {G}eneration {S}equencing {D}ata}",
- Journal="Genetics",
- Year="2013",
- Pages=" ",
- Month="Sep"
- }